Remaining Performance Obligations (RPO) is an essential metric for SaaS companies and their financial stakeholders. It offers a thorough perspective on future revenue potential, providing insights that traditional financial statements may not capture. RPO signifies the total contracted revenue yet to be recognized, including both deferred revenue and backlog.
RPO’s importance has grown significantly since the introduction of ASC 606 for SaaS, the revenue recognition standard that transformed how companies account for contract-based revenue. ASC 606’s focus on performance obligations and contract transparency has made RPO a valuable tool for analysts and investors who need to gauge the long-term growth potential of SaaS companies. High-profile SaaS companies like Salesforce and Adobe now report RPO to provide stakeholders with insights into future revenues.
With RPO, SaaS financial professionals can present anticipated revenue clearly and effectively. By tracking RPO trends, financial experts can evaluate the strength of their sales pipeline and the efficacy of long-term contract strategies. This data, in turn, builds investor confidence and supports strategic initiatives.
Key Takeaways
- RPO offers a detailed view of future contracted revenue for SaaS companies.
- It includes deferred revenue and backlog, providing a richer context than traditional metrics.
- RPO aids in forecasting, strategic planning, and communication with stakeholders.
Understanding Remaining Performance Obligations (RPO)
Remaining Performance Obligation (RPO) is a valuable metric that sheds light on a company’s future revenue potential. It represents the total value of contracted work yet to be completed or recognized as revenue.
Introduction to RPO
RPO is an essential metric for businesses, particularly in the SaaS industry. It captures the total revenue expected from current contracts that have not yet been fulfilled, offering a view into the health of the sales pipeline and future revenue prospects.
For subscription-based businesses, RPO SaaS metric provides a clear snapshot of committed future revenue. By reviewing RPO, companies can assess growth trajectories and make data-driven decisions about resource management and strategic direction. The insights drawn from RPO analysis also allow for better communication with stakeholders, enhancing transparency in financial reporting.
Components of RPO SaaS Metric
RPO includes two main elements: deferred revenue and backlog. Deferred revenue consists of payments received for goods or services that have not been delivered yet, shown as a liability on the balance sheet until the obligation is met.
Backlog refers to contracted work that has yet to begin or be invoiced, encompassing future revenue from signed contracts not recognized as current revenue. Combined, deferred revenue and backlog form total RPO, presenting a comprehensive look at a company’s future revenue landscape.
Understanding these components aids in cash flow forecasting and strategic planning. It also highlights risks and opportunities within the contract portfolio. By analyzing both deferred revenue and backlog, businesses can gain a nuanced understanding of how various contracts contribute to overall financial stability.
Calculating RPO SaaS Metric
Calculating Remaining Performance Obligations (RPO) requires a structured approach to understanding future revenue commitments. This involves careful examination of contract terms and financial data to project revenue streams accurately.
Steps in RPO Calculation
To calculate RPO SaaS Metric, start by identifying all active contracts, noting details like contract duration, billing schedules, and revenue recognition timelines. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Identify Total Contract Value (TCV): For each contract, determine the TCV. Then, subtract any revenue already recognized to arrive at the remaining revenue to be recognized over the contract duration.
- Account for Deferred Revenue and Unbilled Amounts: Deferred revenue reflects payments received for services yet to be delivered, representing obligations still to be fulfilled. Unbilled amounts refer to future payments for contracted services that haven’t yet been invoiced but are part of the committed revenue.
- Consider Contract Length and Billing Cycles: Multi-year contracts introduce additional complexity in RPO calculations, as revenue recognition must be projected over extended periods. Billing schedules, whether monthly, quarterly, or annual, impact when revenue is recognized, so it’s essential to map out these cycles accurately for each contract.
Example Calculation:
Consider a 3-year contract with a TCV of $120,000. If $30,000 has already been recognized in the first year, the remaining $90,000 constitutes the Remaining Performance Obligations. With annual billing, the revenue recognition will occur across the remaining two years, adjusted by any deferred or unbilled amounts.
Given the complexity of managing RPO, financial professionals need access to accurate data. Platforms like Daloopa simplify tracking and calculating RPO and offer seamless integration into financial models.
Importance of Accurate RPO Calculation
Accurate RPO calculation is key for financial forecasting and communicating with stakeholders. It clarifies future revenue streams, aiding CFOs and analysts in identifying growth patterns. This insight is crucial for strategic planning and resource distribution.
Reliable RPO data supports informed decisions on scaling operations, adopting new technologies, or exploring market expansions. It helps set achievable revenue targets and manage investor expectations. The accuracy of these figures also strengthens relationships with stakeholders by showcasing a company’s commitment to transparency and sound financial management.
Misrepresenting RPO can impact a company’s perceived financial health, leading to flawed decisions and reduced investor trust. Regularly reconciling RPO with actual revenue ensures precision and credibility, reinforcing confidence among investors and business partners.
RPO as a Metric for Predicting Future Revenue
Remaining Performance Obligations (RPO) in Saas serve as an effective tool for forecasting revenue in subscription-based businesses, providing a snapshot of revenue trajectory and potential growth.
RPO and Revenue Recognition
RPO encompasses deferred revenue and backlog, showcasing a full view of contracted future revenue. Under ASC 606 for SaaS, deferred revenue covers payments for undelivered services, while backlog includes unbilled contracted amounts. This metric clarifies when obligations are expected to convert into revenue.
Short-term RPO often includes revenue expected within 12 months, while long-term RPO extends beyond that period. Analyzing these figures can reveal the stability of revenue streams and highlight potential changes in future periods. This level of insight helps companies prepare for variations in revenue recognition, ensuring smoother operational transitions and proactive financial adjustments.
RPO’s Role in Strategic Planning
RPO is central to strategic planning and decision-making. Businesses can allocate resources effectively, plan capacity, and shape investment strategies by evaluating the total backlog and structure.
It enables accurate revenue forecasting, offering stakeholders a clearer view of financial health. RPO trends can guide pricing adjustments, highlight growth avenues, and improve sales tactics. Additionally, understanding RPO provides a way to benchmark performance against competitors, refining strategies to maintain a competitive edge.
Assessing RPO alongside bookings and revenue helps gauge the success of marketing and customer retention efforts. This information is essential for refining sales processes and improving overall business strategy.
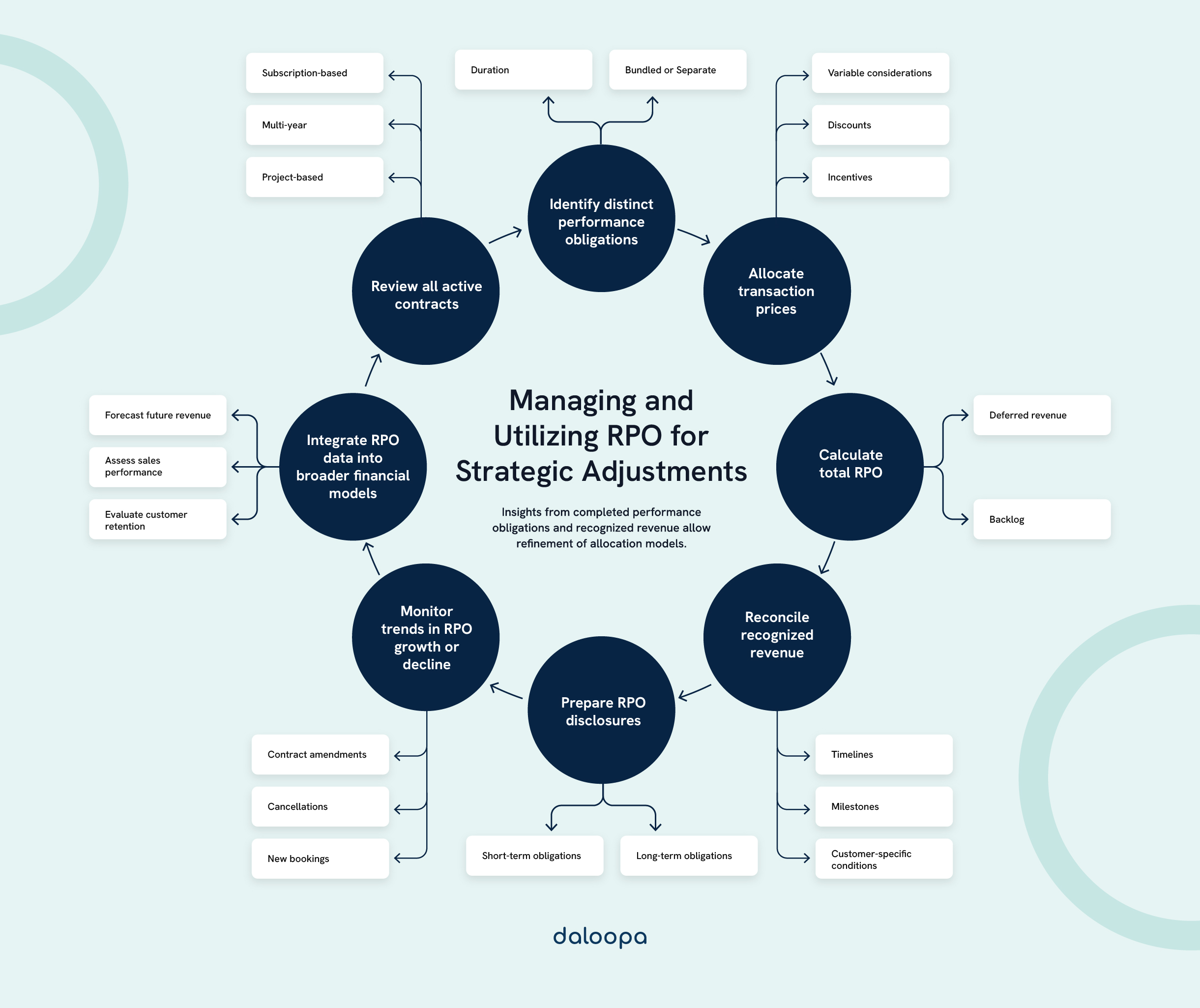
RPO Reporting and Disclosure
Accurate RPO reporting and disclosure are essential for transparency and compliance with accounting standards. Overcoming reporting challenges while following best practices ensures informative RPO disclosures.
Best Practices for RPO Reporting
Effective RPO reporting starts with maintaining detailed contract databases to track obligations. Robust internal controls help verify data accuracy. Clear financial statements distinguishing deferred revenue and backlog are vital.
Consistent disclosure across reporting periods is necessary, with a breakdown of revenue recognition over time. Supplementary information on contract lengths and renewal rates adds transparency. Regular reconciliation with other metrics like bookings and revenue strengthens investor confidence and enhances trust in reported figures.
Challenges in Remaining Performance Obligations Reporting
RPO reporting comes with challenges, especially when dealing with long-term or complex contracts. Accurately estimating revenue recognition timelines involves more than following standard schedules. It requires factoring in variables like implementation delays, customer-specific conditions, and customized billing terms. For example, multi-year SaaS contracts can require updates as terms evolve or performance milestones are achieved.
Another common challenge is determining which contracts qualify for RPO reporting. While ASC 606 provides guidelines, judgment is often needed for certain contracts, particularly with variable considerations, cancellable contracts, and evergreen agreements. Companies must define and consistently apply policies around these contract types to ensure reliable and accurate reporting.
Additionally, balancing transparency with competitive sensitivity can be difficult. Detailed disclosures can offer valuable insights to stakeholders but also risk exposing sensitive information to competitors. Aligning disclosure practices with the overall strategic approach ensures both regulatory compliance and competitive safeguarding.
The Strategic Value of Remaining Performance Obligations
RPO holds significant strategic value for SaaS companies, supporting accurate forecasting and growth assessment.
It outlines contracted revenue not yet recognized, aiding in strategic financial planning. This helps make informed choices about resources and investments.
For investors, RPO shows a company’s financial health, reflecting the sales pipeline’s strength and pricing effectiveness. A growing RPO often indicates solid customer retention and upselling.
RPO is vital for companies with multi-year contracts or complex pricing. It captures long-term contract value, giving a deeper view than metrics like Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR).
Using RPO allows:
- More accurate cash flow forecasts
- Strategic product and marketing decisions
- Informed hiring and capacity planning
- Stakeholder confidence in business stability
Reviewing RPO alongside metrics like Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) offers a full understanding of business efficacy. The integration of these metrics provides a broader perspective on financial health, enabling a more effective approach to long-term planning.
RPO’s insights reveal contract length trends, pricing preferences, and customer habits, guiding strategic adjustments to meet market needs and align with growth objectives. These elements collectively help SaaS businesses stay adaptive and competitive in a dynamic environment.
Using Remaining Performance Obligations for Accurate Forecasting and Financial Confidence
Remaining Performance Obligations (RPO) in SaaS have become indispensable for companies and their stakeholders. It offers a transparent view of future revenue that goes beyond traditional metrics. As SaaS models evolve and ASC 606 for SaaS emphasizes contract clarity, RPO provides detailed insights into sales pipeline health, long-term revenue forecasts, and strategic planning. By understanding and accurately reporting RPO, businesses not only reinforce investor confidence but also refine their operational strategies.
Tracking and calculating metrics like RPO can be challenging, making automated data tools invaluable. Daloopa’s financial data platform simplifies the process, by extracting and delivering comprehensive and current financial data directly to your models. Explore Daloopa today to see how it can save you time and improve accuracy in your financial models.



